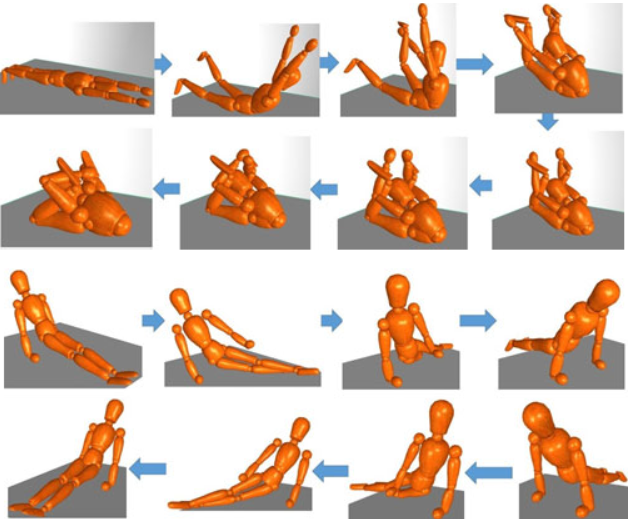
In this paper, we present a local motion planning algorithm for character animation. We focus on motion planning between two distant postures where linear interpolation leads to penetrations. Our framework has two stages. The motion planning problem is
first solved as a Boundary Value Problem (BVP) on an energy graph which encodes penetrations, motion smoothness and user control. Having established a mapping from the configuration space to the energy graph, a fast and robust local motion planning algorithm is
introduced to solve the BVP to generate motions that could only previously be computed by global planning methods. In the second stage, a projection of the solution motion onto a constraint manifold is proposed for more user control. Our method can be integrated
into current keyframing techniques. It also has potential applications in motion planning problems in robotics.
Abstract
Resources
-
, , .
An energy-driven motion planning method for two distant postures.
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG).
2014
Journal
Paper BibTex @article{wang2014energy, author = {He Wang and Edmond SL Ho and Taku Komura}, title = {An energy-driven motion planning method for two distant postures}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG)}, year = {2014} } -
, .
Energy-Based Pose Unfolding and Interpolation for 3D Articulated Characters.
International Conference on Motion, Interaction and Games (MIG).
2011
Conference
Paper BibTex @inproceedings{wang2011energy, author = {He Wang and Taku Komura}, title = {Energy-Based Pose Unfolding and Interpolation for 3D Articulated Characters}, booktitle = {International Conference on Motion, Interaction and Games (MIG)}, year = {2011} }
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers. This work was partially supported by grants from EPSRC (EP/ H012338/1), EU FP7 TOMSY, HKBU Science Faculty Research Grants (FRG1/12-13/055 and FRG2/12-13/078) and the Hong Kong RGC GRF (No. 210813). Previously H. Wang was with the School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, EH8 9AB, UK.